3.Galaxy comparison Method
But, Once a few assumptions were made, we can estimate....
The closest galaxies by themselves provide the equivalent of the Cepheid variable stars.That is, as Hubble saw, galaxies could become the reference points with which astronomers could compare still more distant objects.
To oversimplify astronomers' procedures, imagine that you observe two spiral galaxies that appear to have the same shape, general appearances, speed of rotation, and mass. Astronomers then conclude that the two galaxies may be basically similar in size. But suppose that one of these spiral galaxies covers 10 times the width on the sky than the other; that is, the former has 10 times the angular size of the later. Suppose also that the galaxy with the greater angular size has 100 times the appearent brightness of the other. Then, if we assume thatthe galaxies are much alike, the conclusion follows that the fainter galaxy must be 10 times more farther away has 1/10 the angular size of the closer galaxy. An increase in distance also reduces an object's appearent brightnes, but in proportion to the square of the distance.
That is why the closer galaxy appears not 10 but 100 times brighter than the more distant galaxy.
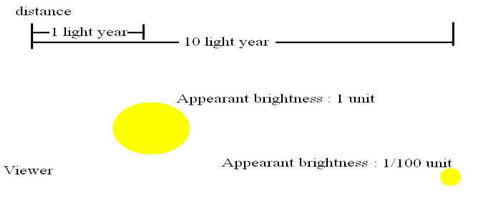
Now if we know the distance to the first spiral - such as the Andremeda galaxy, 2 million light years away - we can then derive the distance to the second galaxy, which in this case would turn out to be 20 million light years. And if we observe a third similarly shaped galaxy whose appearent brightness is only one onehundredth that of the second galaxy, we can conclude - with some caution - that the third galaxy must be 200 million light years away.
Here, some error must inevitably appear at each step. No two galaxies are exatly identical, and even the assumption of close resemblace cannot be directly varified.